compression test cartilage|mechanical testing of cartilage : solution Integration strength increased between 4 and 8 weeks as determined by a . Resultado da 19 de jul. de 2023 · Eylül Tumbar is on Facebook. Join Facebook to connect with Eylül Tumbar and others you may know. Facebook gives people the power to share and makes the world more open and connected.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB2 dias atrás · Smead said in a note on Tuesday. The Nifty Fifty, a group of large mega-cap stocks that dominated the market in the 60s and 70s, ended up plunging in the 1973 market crash. Similarly, Cisco and .
Perhaps the easiest compressive test to perform on cartilage constructs and tissues is the ramp test, which involves the application of a constant compressive strain until a specified strain level is reached.
Creep testing. Systematic review of (A) creep stress and (B) creep relaxation .Integration strength increased between 4 and 8 weeks as determined by a .
2.1. Theoretical Model of Cartilage. A cartilage layer was simulated by a finite .Introduction. Osteoarthritis, the leading cause of severe disability in the United .The six possible steps of the indentation test are illustrated in Fig. 2. To begin the . Schematic representation of an apparatus used to perform a confined compression test (left) and an indentation test (right) on articular cartilage.
Specifically, methods to determine the equilibrium confined compressive (or aggregate) modulus, the equilibrium unconfined compressive (or Young’s) modulus, and the dynamic . The Young's modulus is the most commonly used elastic modulus. It can be measured using the simplest mechanical test (i.e., the compression test, also called unconfined compression test) where samples . The material properties of articular cartilage have been extensively studied using indentation and unconfined compression testing.
research paper on universal testing machine
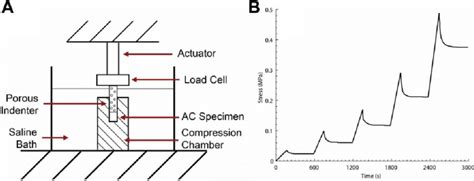
For the confined compression test, a porous plate or indenter is used to let fluid flow out of the tissue. Four test configurations are commonly used to characterize cartilage .properties of tissue engineered cartilage. Specifically, methods to determine the equilibrium confined com-pressive (or aggregate) modulus, the equilibrium unconfined compressive (or .
We performed a systematic in silico parameter sensitivity analysis to find the most efficient unconfined compression testing protocols for mechanical characterization of hydrogel .
For tibial cartilage, compression test results indicate that TMI-M and TLI-M are stiffer than TMI and TLI. This can be explained by the difference in the physiological loading. Physiologically, car-tilage is stressed mainly in compression: this could be the reason why the FDA suggests various kinds of test (tension, shear.), but it gives standard . When used in conjunction with biphasic theory, the confined compression test can be used to estimate material parameters, such as the hydraulic permeability (Armstrong and Mow, 1982; Buschmann et al., 1992).An issue which has arisen in the interpretation of confined compression experiments is the nature of the boundary conditions at the cartilage/porous .Question: A material is being tested as a substitute for cartilage. A compression test (where force is directed down on the top of the material) is performed on a piece of the material with the following shape: The following force vs. length .
structural cartilage testing
In unconfined compression test of articular cartilage at 1000 µm/s, it was found that the total load capacity decreased close to that at equilibrium condition within 30 s after compression. Therefore, we changed elastic property from immediately after compression until about 30 s to conform FEM value to experimental value. When instantaneous . In cartilage biomechanics, instead of Young’s modulus, the aggregate modulus is often used to describe the tissue, because it can be directly calculated from the equilibrium data in a confined compression test (e.g., Figure 4) . The aggregate modulus is a measurement of the stiffness of the tissue at the equilibrium when all fluid flow has .Posthoc tests indicated that the glycosaminoglycan density The confined compression creep test of cartilage is commonly used to assess two physical properties of articular cartilage: the equilibrium confined compression modulus and the hydraulic permeability (1,31). The biphasic theory (31) and linear electrokinetic coupling (12) were used to .
Joints are then grouped based on the exact research question (e.g., age, disease state, treatment group, etc.). Articular cartilage thickness is measured using a needle penetration test; then, either a “double indentation test” or a “platen compression test” is chosen based on the research question and/or the material properties of . Therefore, established methods to test cartilage fracture properties can be used as a guide in testing hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. These tests include the single edge notch (SEN) . the most straightforward evaluation of general toughness for hydrogels is through the compression test, through which the elastic modulus and shear .A positive test may mean that the cartilage under your patella is wearing down. The test is negative if you don’t experience any issues during the test. How do I prepare for the patellar grind test? You don’t have to do anything to prepare for the patellar grind test. It’s a common procedure usually performed in a doctor’s office.
The streaming potential response of cartilage in the confined compression creep configuration was assessed theoretically and measured experimentally in normal and proteoglycan-depleted tissue. The analytical solution, using the linear biphasic continuum model including electrokinetics and assuming homogeneous material properties, predicted that: (i) the peak streaming . We found that the stress responses to the three types of tests were dissimilar, with ramp compression the only test exhibiting linear behavior. Ramp release from a static compression offset was non-linear in a manner such that the cartilage maintained a compressive stress higher than expected by a linear theory. Sinusoidal compression also .
Create Group Test Enter Test Code Active Test Cases. Cases. Cases Search Cases Trauma . (TFCC compression) or radial deviation (TFCC tension) Imaging. Radiographs. usually negative. zero rotation PA view evaluates ulnar variance.
4.2 (a) For the confined compression test on a piece of cartilage, assume that Darcy's law holds; that is where Q is the volumetric flow per unit time, K is the hydraulic permeability coefficient (m'/Ns), A is the cross-sectional area of the specimen, t is the thickness and Δ P is the pressure differential between the top and bottom of the specimen. Aims of the present study were to test the hypotheses that (1) the compressive properties of articular cartilage are affected more by changes in the medium ionic concentration than the tensile properties, (2) collagen network controls the compression–tension nonlinearity of articular cartilage, and (3) proteoglycan (PG) and collagen contents are primary determinants .the mathematics of modeling cartilage is outside the scope of this chapter, some examples illustrate the fundamental fluid– solid interaction in cartilage. MATERIAL PROPERTIES A confined compression test is one of the commonly used methods for determining material properties of cartilage (Fig. 5.4). A disc of tissue is cut from the joint and .
riehle rig universal testing machine
Articular cartilage is frequently modelled as a single-phase, incompressible, elastic solid with an instantaneous elastic response under instantaneous loading, while under sustained deformation, AC exhibits .(b) During the confined compression test, the cartilage sam-ple is placed inside a confining chamber (see Fig. 2a). This prevents fluid from exuding out of the sample in the radial direction. In addition, the sample cannot bulge in the radial direction. A rigid porous indenter (e.g., a steel or The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a load-bearing structure between the lunate, triquetrum, and ulnar head. The function of the TFCC is to act as a stabilizer for the ulnar aspect of the wrist. The TFCC is at risk for either acute or chronic degenerative injury. Forced ulnar deviation and positive ulnar variation carry associations with injuries to the TFCC. . We performed a systematic in silico parameter sensitivity analysis to find the most efficient unconfined compression testing protocols for mechanical characterization of hydrogel constructs and cartilage explants, with a minimum number of tests but maximum identifiability of the material parameters. The construct and explant were thereby modelled as .
Cartilage is an important part of your ability to stand, move and do anything else that uses your joints and bones. It absorbs shocks and helps your bones move smoothly. If you injure your cartilage — especially in a joint — it might take a while to recover. But don’t rush your body’s healing process.The patella is a triangular shaped sesamoid bone, the posterior surface of the patella is covered with articular cartilage. . Compression test. Tests for patellofemoral joint degeneration. The patella is compressed as the patient flexes his knee. A .2- (30 points) A confined compression test is performed on a cartilage tissue. This test is conducted in a closed cylindrical chamber where the cartilage sample completely fills the chamber volume. A porous piston is used to apply force F to the sample very slowly to allow the liquid flow slowly out of the sample.The stress-strain relationship of cartilage in compression was observed previously to depend on the strain-rate. This strain-rate dependence has been thought to originate mainly from fluid pressurization. . Indentation Test Seventeen cartilage-bone blocks, with intact cartilage surface, were harvested from the trochlear groove of two .
To perform the TFCC Compression Test according to Prosser et al. in the year 2011, fixate your patient’s radius and ulna with one hand close to the joint line. Then grab your patient’s hand at the height of the meta-carpals from radial and bring his wrist .We performed ex vivo testing of two equine patellas with healthy cartilage, one with superficial defects, and one with synthetically degenerated cartilage to simulate a pre-osteoarthritic stage. Static compression with 400 N for 2 h resulted in morphological changes comparable to physiological in vivo deformations in humans. The O’Brien test, or active compression test, is a simple procedure to assess the cause of shoulder pain. If you experience pain or clicking during the test, you may have a torn labrum or an abnormality in your acromioclavicular (AC) joint. . Your labrum is a bumper-shaped piece of cartilage that lines the rim of the socket bone of your .there's a uniaxial compression test where a cylindrical sample of articular cartilage with height = 1.5 mm, diameter = 3 mm is subjected to 0.5 N of uniaxial compressive force in a creep test (compression is applied in the direction of the height dimension). Using the standard linear solid model, find E1, E2, and the time constant for this .
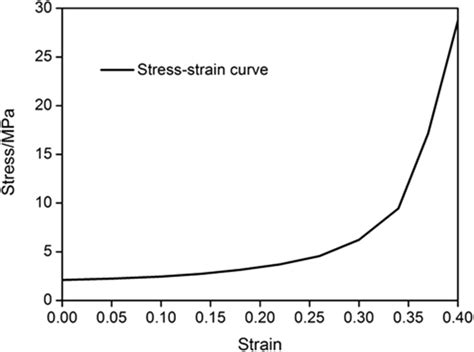
stress strain curve cartilage
Unlabelled: In a series of 103 specimens from the lateral facet of the human patella, the intrinsic mechanical properties of articular cartilage were measured using a confined compression creep test.
mechanical testing of cartilage
knee cartilage testing guidelines
Best Videos - 'madrasta rabuda' Search - XVIDEOS.COM
compression test cartilage|mechanical testing of cartilage